Astronomy
Astronomy
The study of all classes of celestial object, such as planets, stars, and
galaxies, as well as interstellar and intergalactic space, and the universe as
a whole. The branch of classical astronomy concerned with the precise
measurement of the positions of celestial objects is known as astrometry.
Modern astronomy began 450 years ago with Copernicus, who set the scene for the
overthrow of the Hellenistic cosmology, asserting that the Sun, not the Earth,
is at the centre of the Solar System. Newton described gravitational theory in
the 17th-c, and thence forth planetary astronomy became an exact science. In
the 18th-c and 19th-c. techniques to build large telescopes were developed,
culminating in the construction of observatories on mountain sites in the USA.
Radio astronomy emerged rapidly after World War 2, and was the first of the
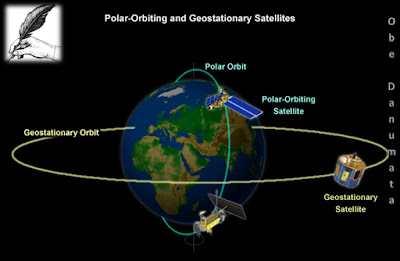
invisible astronomies. The use of satellites above the blanket of the Earth's
atmosphere enabled ultraviolet, X-ray, and infrared astronomies to be developed
from the 1960s.





Comments
Post a Comment